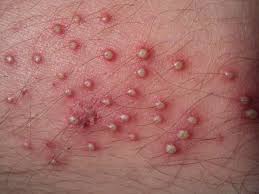
It is a common skin condition in which hair follicles become inflamed usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. The infection can spread and turn into non healing, crusty sores.
Folliculitis
It is a common skin condition in which hair follicles become inflamed usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. The infection can spread and turn into non healing, crusty sores.
Symptoms:
· Clusters of small red bumps or white-headed pimples that develop around hair follicles
· Pus-filled blisters that break open and crust over
· Itchy, burning skin
· Painful, tender skin
· A large swollen bump or mass
Types of Folliculitis:
· Bacterial folliculitis. This common type is marked by itchy, white, pus-filled bumps. It occurs when hair follicles become infected with bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus (staph).
· Hot tub folliculitis (pseudomonas folliculitis). Pseudomonas bacteria, causes this type of disorder, found in many places, including heated pools and hot tubs in which the chlorine and pH levels aren't well-regulated.
· Razor bumps (pseudofolliculitis barbae). This is a skin irritation caused by ingrown hairs. It mainly affects men with curly hair who shave too close and is most noticeable on the face and neck.
· Pityrosporum (pit-ih-ROS-puh-rum) folliculitis. This type is caused by a yeast infection. Chest and back and sometimes on the upper arms, neck, shoulders and face produces red, chronic, itchy pustules.
Causes: Folliculitis is caused by an infection of hair follicles with Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria, viruses, fungi and even an inflammation from ingrown hairs.
Risk factors:
· Having acne or dermatitis, diabetes, chronic leukemia and HIV/AIDS
· Being a male with curly hair who shaves
· Taking long-term antibiotic therapy for acne or steroid creams.
· Soaking in a hot tub that's not maintained well
· Causing damage to hair follicles by shaving, waxing or wearing tight clothing
Complications:
· Recurrent or spreading infection
· Hair follicles destruction and permanent hair loss
· Boils under the skin (furunculosis)
· Permanent skin damage, such as scarring or dark spots
Prevention:
· Avoid tight clothes. It helps to reduce friction between your skin and clothing.
· Dry out rubber gloves between uses.
Diagnosis: Your doctor is likely to diagnose folliculitis by looking at your skin and reviewing your medical history and dermoscopy.
Treatment:
· Creams, shampoos or pills to fight fungal infections. Antifungals are for infections caused by yeast rather than bacteria. Antibiotics aren't helpful in treating this type.
· Creams or pills to reduce inflammation. If you have HIV/AIDS, you may see improvement in your eosinophilic folliculitis symptoms after antiretroviral therapy. Try a steroid cream to ease the itching for mild eosinophilic Folliculitis.
Other interventions:
Folliculitis, hair follicles, bacteria, fungus, crusty sores.