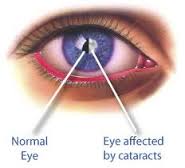
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. It can affect one or both eyes. Often it develops slowly. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night.
Cataracts
A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of eye. For people who have cataracts, seeing through cloudy lenses is a bit like looking through a frosty or fogged-up window. Most of the cataracts don't disturb eyesight early on and are developed slowly.
Symptoms:
· Clouded, blurred or dim vision
· Increasing difficulty with vision at night
· Sensitivity to light
· Frequent changes in contact lens or eyeglass
· Fading or yellowing of colors
· Double vision in a single eye
Causes:
Formation of cataract: The lens, where cataracts form, is positioned behind the colored part of eye (iris). The light-sensitive membrane in the eye functions as the film in a camera, the lens focuses light that passes into the eye, producing sharp and clear images on the retina. As the age, the lenses in the eyes become less flexible, less transparent and thicker. Medical conditions, age-related and other cause’s break down of the lens tissues within the lens.
As the cataract continues to develop, scatters and blocks the light as it passes through the lens, preventing a sharply defined image from reaching retina and the cloud becomes denser and involves a bigger part of the lens. As a result, the vision becomes blurred.
Types of cataracts:
· Nuclear cataracts (Cataracts affecting the center of the lens): A nuclear cataract may at first cause more nearsightedness or even a temporary improvement in reading vision. As the cataract slowly progresses, the lens may even turn brown.
· Posterior sub capsular cataracts (Cataracts that affect the back of the lens): This type of cataract starts as a small, opaque area that usually forms near the back of the lens, right in the path of light. A posterior sub capsular cataract often interferes with the vision during reading, causes halos or glare around lights at night. These types of cataracts tend to progress faster than other types do.
· Cortical cataracts (Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens): A cortical cataract begins as wedge-shaped streaks or opacities, whitish, on the outer edge of the lens cortex. As it progresses slowly, the streaks extend to the center and interfere with light passing through the center of the lens.
· Congenital cataracts: Some people are born with cataracts or develop them during childhood. These cataracts may be associated with an intrauterine infection, or genetically, or by trauma.
Risk factors
· Exposure to sunlight
· Increasing age
· Diabetes
· Smoking
· Previous eye inflammation or injury
· Obesity
· Previous eye surgery
· High blood pressure
· Prolonged use of corticosteroid medications
· Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
Diagnosis:
· Visual acuity test: A visual acuity test uses an eye chart to measure how well you can read a series of letters. Eyes are tested one at a time, while the other eye is covered. Using a chart or a viewing device with progressively smaller letters, ophthalmologist determines if the people have 20/20 vision or vision shows signs of impairment.
· Slit-lamp examination: A slit lamp allows to see the structures at the front of eye under magnification. The microscope is called a slit lamp because it uses an intense line of light, a slit, to illuminate your cornea, iris, lens, and the space between iris and cornea.
· Retinal exam: To prepare for a retinal exam, doctor puts drops in a eyes to open pupils wide (dilate). This makes it easier to examine the back of eyes (retina). Using a slit lamp or a special device called an ophthalmoscope, doctor can examine lens for signs of a cataract.
Treatment:
When prescription glasses can't clear the vision, the only effective treatment for cataracts is surgery.
Cataract surgery: Cataract surgery involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with a clear artificial lens. The intraocular lens (artificial lens) is positioned in the exact place of a natural lens. It remains a permanent part of eye.
Cataract surgery is generally safe, but it has a risk of bleeding and infections.
Prevention:
Cataracts, opaques, blurred vision, nuclear cataracts, cortical cataracts