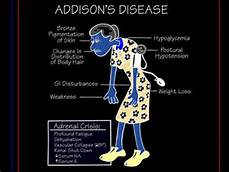
Addison’s disease (also known as primary adrenal insufficiency or hypoadrenalism) is a rare disorder of the adrenal glands.
Addison’s disease
It is also called as an adrenal insufficiency, it occurs when the body produces insufficient amounts of certain hormones produced by adrenal glands. In this disease, adrenal glands produce insufficient levels of aldosterone and often too little cortisol as well. It can be life-threatening and occurs in all age groups and affects both sexes.
Causes: Addison's disease results when adrenal glands are damaged, producing insufficient amounts of the hormone cortisol and often aldosterone as well. Other infections of the adrenal glands, Spread of cancer to the adrenal glands, Secondary adrenal insufficiency, Tuberculosis.
Symptoms: Abdominal pain, Extreme fatigue, Low blood pressure, hyper-pigmentation (Darkening of skin), Weight loss and decreased appetite, even fainting, Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, Depression, Acute adrenal failure (addisonian crisis).
Diagnosis:
Treatment:
Addisons, endocrine disorder, adrenal insufficiency