Alzheimer's Disease
 It is a progressive neurodegenerative brain disorder damages brain cells, leads to impaired memory, thinking and behavior.
It is a progressive neurodegenerative brain disorder damages brain cells, leads to impaired memory, thinking and behavior.
Symptoms: It is a rare genetical condition, symptoms of Alzheimer's disease vary person to person.
- Common condition is memory loss
- Confusion in planning, problem solving, events, time and place
- Disorientation
- Mood and behavior changes
- Difficulty in speaking, swallowing and walking
- Problem in finding the objects
- Depression
- Apathy
- Irritability and aggressiveness
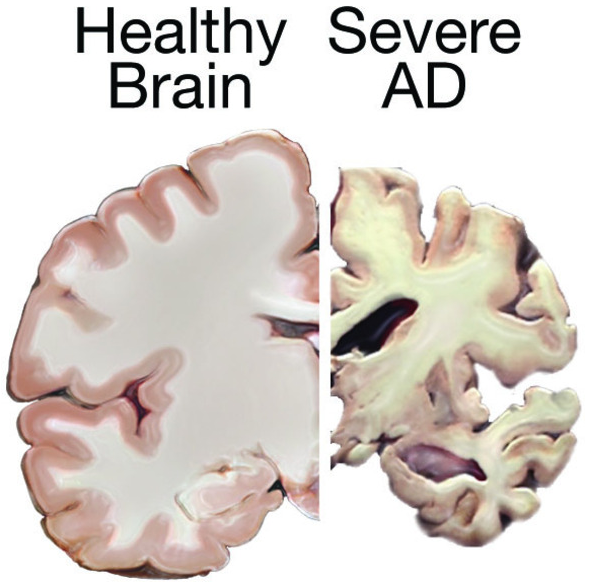
Causes: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) caused by shrinking of brain tissue due to formation of plaques and tangles.
- Plaques: Accumulation of myeloid proteins interferes with cell-to-cell communication and destroys healthy cells.
- Tau proteins: These are internal transport proteins carries nutrients to different parts of brain but in abnormal condition tau proteins twists into abnormal tangles in brain cells, leads to failure of the transport system.
Risk Factors: Several multiple factors involved in developing AD.
- Age: Well known risk for AD is getting older and the condition doubles after every 5 years once you reach 60 years.
- Down syndrome: One of the genetical risk factor develops plaques in brain cells.
- Head Injury: People who have had a major head injury have the greater risk for AD.
- Family History: Parents and siblings with AD are strong risk factors.
- Heredity: Common forms of APOE gene may be a risk factor for AD.
Diagnosis: Clinically relevant brain neuroimaging findings in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
- Computerized Tomography: Used to assess tumors, strokes and head injuries.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Check for microscopic β-amyloid neuritic plaques and nuerofibrillary tangles.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): A radioactive form of sugar is used to assess levels of amyloid and tau proteins.
- Cerebro Spinal Fluid: Checked for excess levels of tau proteins by biomarkers.
Treatment: Biochemical mechanism of AD is not well understood, so, individual basis management for each symptom. Use of NSAIDS, BACE inhibitors, estrogens, nerve growth factors, statins, and antioxidants are in under review.
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: Inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine in brain cells, which accelerates cell-to-cell communication temporarily.
- NMDA receptor: Excess release of glutamate levels destroys brain cells. Use of administration of NMDA receptor antagonists block the effects of excess glutamate.
- Exercise: Regular physical activities like walk improves mood and keeps healthy joints, muscles and heart.
- Nutrition: Healthy shakes, water, juice, high-calorie supplements helps to AD patients for better health.
It is a progressive neurodegenerative brain disorder damages brain cells, leads to impaired memory, thinking and behavior.
It is a progressive neurodegenerative brain disorder damages brain cells, leads to impaired memory, thinking and behavior.