Myositis
Introduction
Myositis condition refers to the inflammation of the muscles.
Types of Myositis:
Myositis classified based on laboratory and clinical differences.
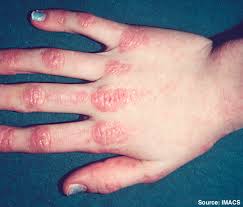
- Dermatomyositis (DM): It affects any type of age between 40 to 60 population and common in women than men and rare to children.
- Rash on eyelids, cheeks, nose, back, upper chest, elbows, knees and knuckles
- Scaly, dry or rough skin
- Trouble rising from a seated position, or getting up after a fall
- General tiredness
- Inflamed or swollen area around fingernails
- Painful and/or itchy rash caused by inflammation of blood vessels under skin and in muscles
- Sudden or progressive weakness in muscles in neck, hip, back and shoulder muscles
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), a feeling of choking
- Hardened lumps or sheets of calcium, called calcinosis, under the skin
- Changes in voice (dysphonia), especially hoarseness
- Inclusion body Myositis (IBM): Common in men than in women after age 50. Slowly develops for months and therapies under trails.
- Frequent falling episodes
- Trouble climbing stairs or standing from a seated position
- A foot that seems to drop when walking, causing tripping
- Weakened hand grip
- Difficulty swallowing
- Weakness and shrinking of the quadriceps (main muscle of the thighs), causing falls
- Weakness in the forearm muscles
- Weakness of muscles below the knees, causing the foot to drop and toes to catch when walking
- Weakness of flexor muscles of the fingers used for gripping
- Weakness of throat muscles, causes dysphagia and possibly choking
- Pain or discomfort as muscles weaken
- Juvenile forms of Myositis (JM): Mostly found in children at the age of 18 and it is very rare. Distinguished by muscle weakness and skin rash.
- Visible, reddish-purple rash over the eyelids or joints
- General tiredness and irritability
- Complaints of tummy aches
- Trouble climbing stairs; standing from a seated position; getting dressed; lifting head
- Difficulty reaching up, like to shampoo or comb hair
- Swelling or redness in the skin around the fingernails
- Characteristic reddish-purple rashes of JM-Gottron's papules and heliotrope rash
- Gradual muscle weakness, most often of those closest to the body like neck, stomach, upper arms and legs
- Hardened lumps or sheets of calcium (calcinosis) under the skin
- Dysphagia
- Dysphonia
- Stomach problems
- Polymyositis (PM): Majorly found in age above 20 years and common in women. Usually happens over days, weeks or months. Reason for PM is may be autoimmune diseases.
- Muscle weakness developed slowly
- Chronic dry cough
- Dysphagia
- Falling and difficulty getting up from a fall
- General feelings of tiredness
- Marked weakness in muscles like forearms, thighs, hips, shoulders, neck and back.
- Weakness in finger and toes
- Thickening of the skin on hands
Causes: It can be caused by injury, infection, autoimmune disease, certain medicines, exercise, and chronic diseases.
Diagnosis: A physician should check patient’s family history and results of careful physical examination. This may be followed by some lab tests, electric activity inside the cells and finally a muscle biopsy if necessary.
- Conventional blood tests: This test should be performed for checking high levels of muscle enzymes like creatine kinase (CK) that releases the muscle fiber when fibers are being damaged. This enzyme levels are very high in Dermatomyositis condition.
- Antinuclear Antibodies test (ANA): ANA test investigated for specific antibodies produced in Myositis conditions and other autoimmune diseases.
- Muscle and skin biopsy: Small samples of muscle tissue or skin examined for abnormalities in muscles, inflammation, damage, and abnormal proteins.
- Magnetic resonance Image Scan (MRI): Magnetic resonance images detect inflammation of muscles and where muscle fibers are replaced by fat or fibrous tissue.
- Electro-diagnostic tests: An electromyogram, involves a tiny electrode is inserted into the muscle to test electric signals from both at rest and when the person tries to contract the muscle. An abnormal pattern of electrical activity may indicates PM or DM.
Medical Management:
- Exercise and Physiotherapy: We must be careful while doing exercises in Myositis conditions. To avoid muscles stiffening gentle muscle and joint movement is very important in children. Low doses of medication help to suppress the autoimmune attack throughout their lives. Avoidance of sun exposure during peak hours and use of sunblock and protective clothing are worsening the skin related diseases.
- Steroid medication: Using steroids in PM and DM. Steroid creams are used treat affected areas in DM.
- High dosage levels of steroid tablets used for treating severe muscle weakness.
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Suppresses the over response of immune system and reduces inflammation.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: This therapy rarely used in severe cases causing life-threatening breathing or swallowing problems. It includes injection of normal antibodies to change temporarily response of immune system. It is very expensive and the benefit lasts for few weeks.
Supplements:
- Coenzyme Q10 – Low levels of CoQ10 are found in Myositis patients. Hence supplementation of Co Q10 may reduce the complications without side effects.
- Creatine – Improves athletic performance and increases the muscle bulk in athletes and older people.
- Fish oil – Omega 3-fatty acids from fish oil are suggestible in to decrease rate of inflammation.
- Ginger and turmeric has strong anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory properties and relieves pain.
- Glucosamine – Promotes the synthesis of proteins in muscles, tendons, cartilage, ligaments and in blood vessels.