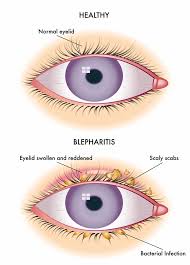
Blepharitis
It is the inflammation of the eyelids, usually involves the part of the eyelid where the eyelashes grow and affects both eyelids.
Blepharitis occurs commonly when the tiny oil glands located near the base of the eyelashes become clogged. This leads to red and irritated eyes. Blepharitis is a chronic condition that is difficult to treat. Several diseases and conditions can cause blepharitis.
Symptoms:
- Itchy eyelids
- A gritty, burning or stinging sensation in the eyes
- Watery eyes
- Red eyes
- Eyelids that appear greasy
- Red, swollen eyelids
- Crusted eyelashes upon awakening
- Flaking of the skin around the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Eyelid sticking
- More frequent blinking
- Loss of eyelashes
Causes:
- allergic reactions to eye
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Rosacea
- A bacterial infection
- Clogged or malfunctioning oil glands in your eyelids
- Eyelash mites or lice
Complications:
- Eyelash problems: Blepharitis can cause your eyelashes to fall out or grow abnormally.
- Eyelid skin problems: Scarring occurs on eyelids in response to the long-term blepharitis or the eyelid edges may turn inward or outward.
- Chronic pink eye: Blepharitis can lead to recurrent bouts of pink eye (conjunctivitis).
- Excess tearing or dry eyes: Abnormal oily secretions and other debris shed from the eyelids, such as oil and mucus solution that forms tears, flaking associated with dandruff, can accumulate in tear film the water. Abnormal tear film interferes with the healthy lubrication of eyelids. This can irritate your eyes and cause symptoms of excess tearing or dry eyes.
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses: Because blepharitis wearing contact lenses may be uncomfortable and can affect the amount of lubrication in eyes.
- Sty: It is an infection that develops near the base of the eyelashes. This results a painful lump on the edge of eyelid. A sty is usually most visible on the surface of the eyelid.
- Chalazion: A chalazion occurs when there's a blockage in one of the small oil glands at the margin of the eyelid, just behind the eyelashes. The gland can become infected with bacteria, which causes a red and swollen eyelid
- Injury to the cornea: Constant irritation from inflamed eyelids or misdirected eyelashes may cause an ulcer (sore) to develop on cornea.
Diagnosis:
- Examination of eyelids
- Swabbing skin for testing
Treatment:
- Self-care measure: Such as washing the eyes and using warm compresses
- Medications that fight infection: Antibiotics applied to the eyelid have been shown to provide relief of symptoms and resolve bacterial infection of the eyelids. These are available in a variety of forms, including creams, eye drops, and ointments.
- Medications to control inflammation: Steroid eye drops or ointments may help to control the inflammation. The doctor may prescribe both the antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Medications that affect the immune system: Topical cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that has been shown to offer relief of some signs and symptoms of blepharitis.
- Treatments for underlying conditions: Blepharitis caused by rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, or other diseases may be controlled by treating the underlying disease.