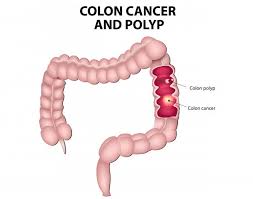
It is the cancer of the colon (large intestine); it is the lower part of digestive system. Rectal cancer is cancer of the last several inches of the colon. Together, they're often referred to as colorectal cancers.
Colon cancer
It is the cancer of the colon (large intestine); it is the lower part of digestive system. Rectal cancer is cancer of the last several inches of the colon. Together, they're often referred to as colorectal cancers.
Symptoms:
· Change in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation or a change in the consistency of your stool, that lasts longer than four weeks
· Persistent abdominal discomfort, such as gas, cramps or pain
· Rectal bleeding or blood in stool
· A feeling that bowel doesn't empty completely
· Weakness or fatigue
· Unexplained weight loss
Risk factors
· Inherited syndromes that increase colon cancer risk
· Older age
· A personal history of colorectal cancer or polyps
· Inflammatory intestinal conditions
· Low-fiber, high-fat diet
· Family history of colon cancer
· A sedentary lifestyle
· Obesity
· Diabetes
· Smoking
· Alcohol
Diagnosis:
Stages of colon cancer:
· Stage 1: Cancer has grown through the mucosa (superficial lining) of the colon or rectum but hasn't spread beyond the rectum or colon wall.
· Stage 2: Cancer has grown through or into the wall of the rectum or colon but hasn't spread to nearby lymph nodes.
· Stage 3: It has invaded nearby lymph nodes but isn't affecting other parts of body yet.
· Stage 4: It is spread to distant sites, such as liver or lung.
Treatment: Depending upon the stage of cancer treatment plan will make. Treatment options for colon cancers are surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.
Surgery:
· Removing polyps during colonoscopy: If cancer is small, localized in a polyp and in a very early stage, doctor may be able to remove it completely during a colonoscopy.
· Minimally invasive surgery: In this procedure, surgeon performs the operation through several small incisions in abdominal wall, inserting instruments with attached cameras that display colon on a video monitor. The surgeon may also take samples from lymph nodes in the area where the cancer is located.
· Endoscopic mucosal resection: Removing larger polyps may require also taking a small amount of the lining of the colon in a procedure called endoscopic mucosal resection.
· Lymph node removal: Nearby lymph nodes are usually also removed during colon cancer surgery and tested for cancer.
Surgery for advanced cancer: If cancer is very advanced or overall health is very poor, surgeon may recommend an operation to relieve a blockage of your colon or other conditions in order to improve symptoms. This surgery isn't done to cure cancer, but instead to relieve signs and symptoms, such as bleeding and pain.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy for colon cancer is usually given after surgery if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. In this way, chemotherapy may help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence. Chemotherapy may be used before surgery to shrink the cancer before an operation.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses powerful energy sources, such as X-rays, to kill cancer cells that might remain after surgery, to shrink large tumors before an operation so that they can be removed more easily, or to relieve symptoms of colon cancer and rectal cancer.
Targeted drug therapy: Drugs that target specific defects that allow cancer cells to grow are available to people with advanced colon cancer, including:
· Cetuximab (Erbitux)
· Bevacizumab (Avastin)
· Ramucirumab (Cyramza)
· Panitumumab (Vectibix)
· Ziv-aflibercept (Zaltrap)
· Regorafenib (Stivarga)
Alternative medicine: No complementary or alternative treatments have been found to cure colon cancer. Alternative treatments that may help relieve distress include:
· Art therapy
· Dance or movement therapy
· Exercise
· Meditation
· Music therapy
· Relaxation exercises
Colon cancer, symptoms, stages, treatment, surgery